SIP Condition Syntax
This appendix describes the syntax to be used to define a SIP Condition. SIP Condition Rule parts are:
| ■ | Subject |
| ■ | Operator |
| ■ | Values |
| ■ | Description |
Subject
Syntax
<Header>/<Tags>/<Source URI>/<Dest URI>/<Http>/<regexGroupFromCondition>
The Condition is used to test specific parts of a SIP header / Tags / Source URI /Dest URI/<Http>/<regexGroupFromCondition>.
The string is case-insensitive.
Param
Syntax:
Param.SecureLogix.<SecureLogixParam>
Where:
SecureLogixParam values are: Score, ActionDirective, RedirectTo.
For example: Param.SecureLogix.ActionDirective
Action Value
| Action Subject | Action Typese |
|---|---|
| Parm.SecureLogix. Score | Modify |
| Param. SecureLgoix.ActionDirective | Modify |
| Param.SecureLogix.RedirectTo | Modify: Add Prefix, Add Suffix, Remove Prefix, Normalization |
For example:
The following SIP Manipulation runs a SIP Condition before creating new header called X_ SLXSCORE.
If Param.SecureLogix.Score exists, its value will be stored in the X_ SLXSCORE header.
Header
Syntax:
header.<header-name>.<attribute>
Where:
| ■ | <header-name> specifies the header name as it arrives in the message. For example: From, To, etc. |
| ■ | <attribute> specifies a specific part of the message. For example: url.user, url.host, etc. |
The Header can be one of the following:
| ■ | Header.From |
| ■ | Header.From.URL.User |
| ■ | Header.From.URL.Host |
| ■ | Header.From.Name |
| ■ | Header.To |
| ■ | Header.To.URL.User |
| ■ | Header.To.URL.Host |
| ■ | Header.To.Name |
| ■ | Header.P-Asserted-Identity |
| ■ | Header.P-Asserted-Identity.URL.User |
| ■ | Header.P-Asserted-Identity.URL.Host |
| ■ | Header.P-Asserted-Identity.Name |
| ■ | Header.P-Asserted-Identity.TelNumber |
| ■ | Header.P-Preferred-Identity |
| ■ | Header.P-Preferred-Identity.URL.User |
| ■ | Header.P-Preferred-Identity.URL.Host |
| ■ | Header.P-Preferred-Identity.Name |
| ■ | Header.Diversion |
| ■ | Header.Diversion.URL.User |
| ■ | Header.Diversion.URL.Host |
| ■ | Header.Diversion.Name |
| ■ | Header.Referred-By |
| ■ | Header.Referred-By.URL.User |
| ■ | Header.Referred-By.URL.Host |
| ■ | Header.Referred-By.Name |
| ■ | Header.Refer-To |
| ■ | Header.Refer-To.URL.User |
| ■ | Header.Refer-To.URL.Host |
| ■ | Header.Refer-To.Name |
| ■ | Header.History-Info |
| ■ | Header.Request-URI |
| ■ | Header.Request-URI.URL.User |
| ■ | Header.Request-URI.URL.Host |
For other headers, the syntax is header.<header-name>
For example: header.my-header
Tags
Syntax:
Tags.TAG_<index>
Where:
Index values are: 1,2,3.
For example: Tags.TAG_1
Source URI
Syntax:
SourceUri .User/Host
For example: SourceUri .Host
Dest URI
Syntax:
DestUri.User/Host
For example: DestUri.User
Http
Syntax: Http.<request/response>.<attribute>
Where:
| ■ | <request/response> specifies whether it is the request or response. |
| ■ | <attribute> specifies a specific part of the request/response. |
These are the available options:
| ● | Http.Response.Status |
| ● | Http.Response.Body |
| ● | Http.Response.Body.FieldName |
| ● | Http.Request.otherHeader |
regexGroupFromCondition
Syntax: regexGroupFromCondition[$1-$6]#
Where:
| ■ | [$1-$6] Specifies which group to take from the last regex operation. |
Operator
The following table describes the condition operators.
|
Condition Operand |
Description |
|---|---|
|
== |
Tests for equivalent values. |
|
!= |
Tests for not equivalent values. |
|
>= |
Tests for greater than or equal to values. |
|
<= |
Tests for less than or equal to values. |
|
> |
Tests for greater than values. |
|
< |
Tests for less than values. |
|
Contains |
Tests a string containing specified text. |
|
Doesn’t contain |
Tests a string not containing specified text. |
|
suffix |
Tests whether a string has a particular suffix. |
|
prefix |
Tests whether a string has a particular prefix. |
|
len > |
Tests whether the length of a string is greater than a specific value. |
|
len < |
Tests whether the length of a string is less than a specific value. |
|
len == |
Tests whether the length of a string is equal to a specific value. |
|
regex |
Tests whether a string matches the given regular expression. |
|
Exists |
Tests whether a parameter exists. |
|
Doesn’t exist |
Tests whether a parameter does not exist. |
|
Prefix Group |
Tests whether a parameter belongs to a specific prefix group. |
Values
Syntax
<Value> [+ <Value>]*|
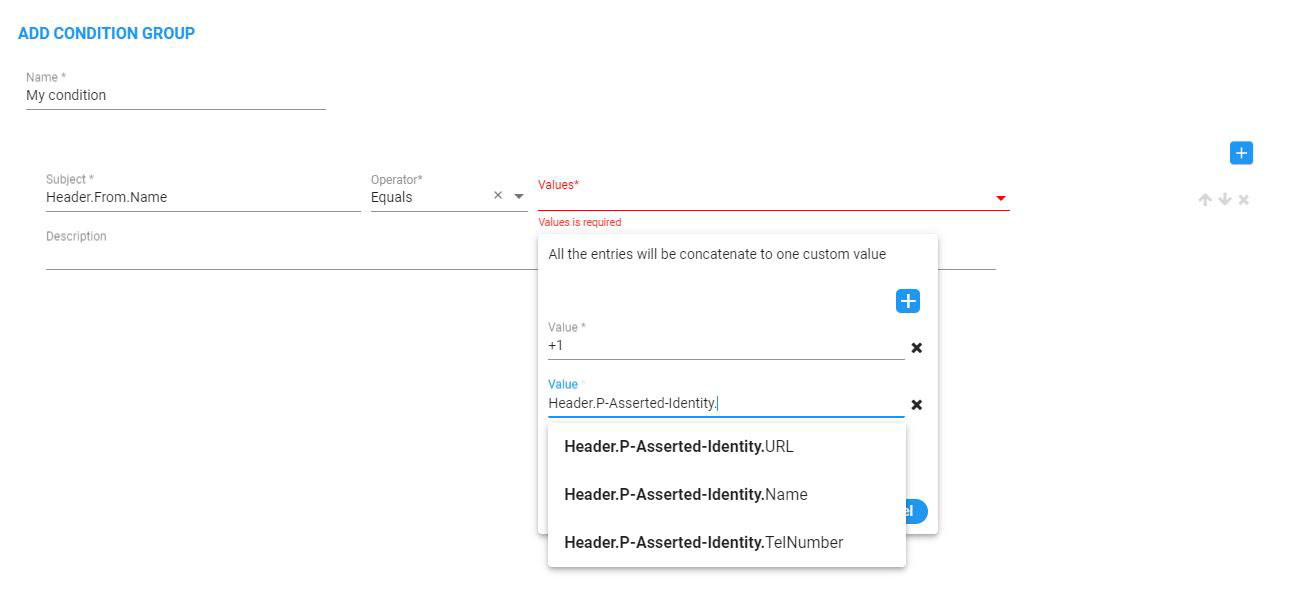
To concatenate values, use the plus “+” operator.
For example, ‘+1’ + header.from.url.user
Value
Syntax
< Subject>/String/prefix group
Where:
String – free string. Must be enclosed by a single quotation mark ('...').
The value should be empty for exist / !exists operators.
The value should be a single string format for Regex operator.
The value should be a Prefix Group for PrefixGroup operator.
The ARM UI provides an auto completion wizard to configure the SIP Condition.
Auto Completion Subject

Auto Completion Value
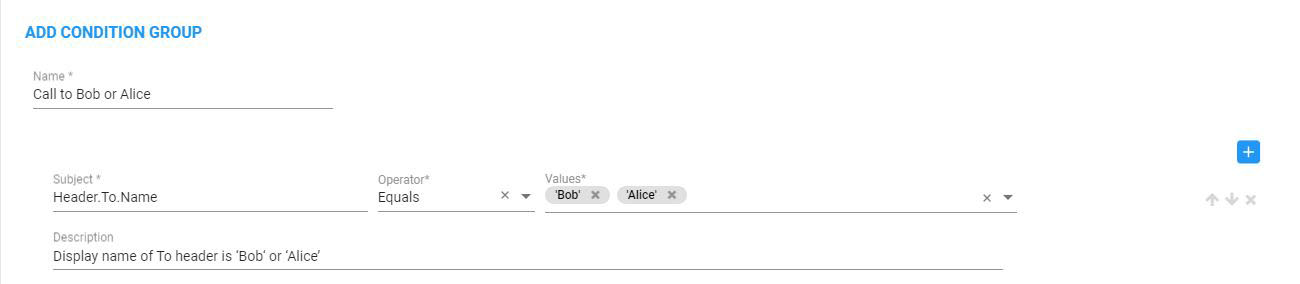
Example 1
The following SIP Condition returns true if the display name of To header is ‘Bob‘ or ‘Alice’:
Or Condition
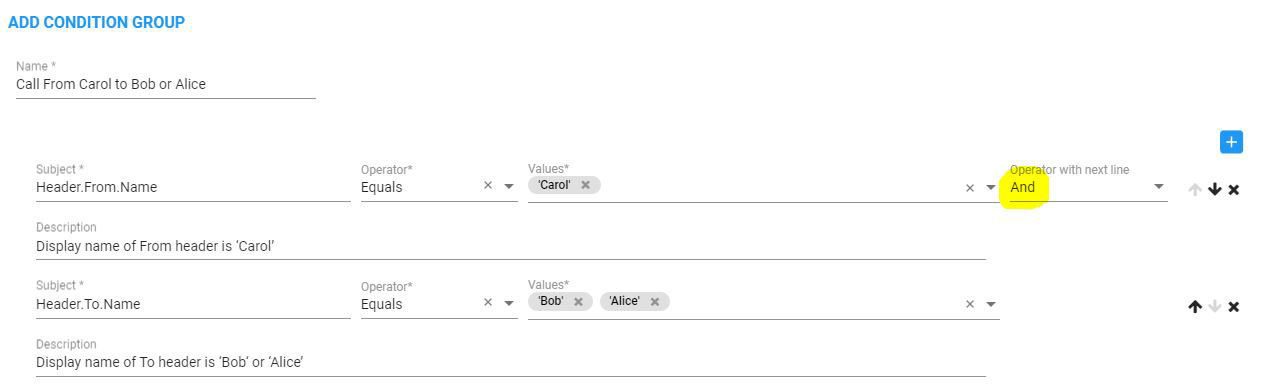
Example 2
The following SIP Condition returns true if the display name of From header is ‘Carol’, and the display name of To header is ‘Bob‘ or ‘Alice’:
And Operator Condition
Example 3
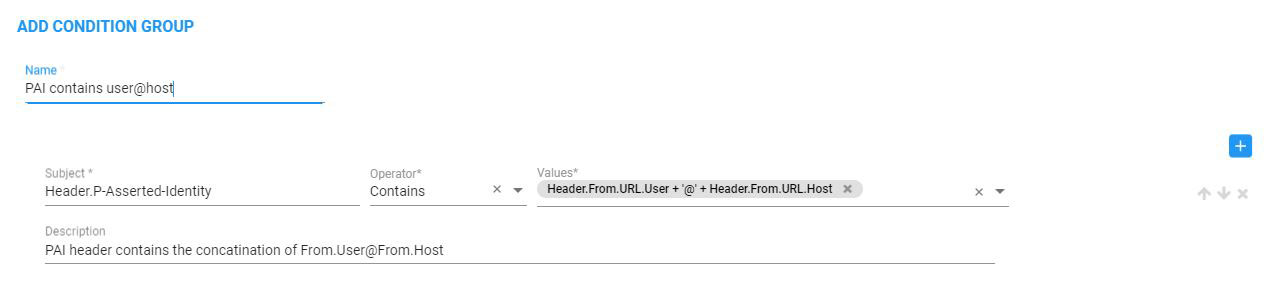
The following SIP Condition returns true if the P-Asserted-Identity header contains the concatenation of:
| ■ | User part of From header |
| ■ | @ |
| ■ | Host part of From header |
Concatenation Strings
Example 4
The following SIP Condition returns true if the ‘X-My-Header’ header exists:
Other Header

Example 5
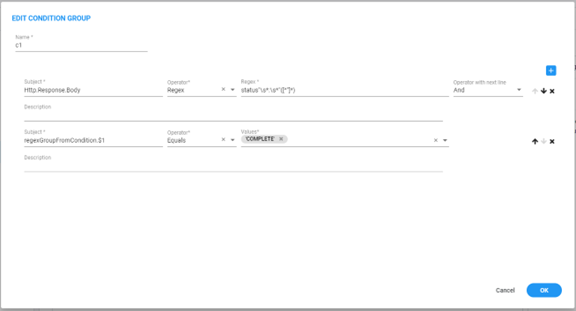
The following Sip Condition does the following things:
| ■ | In the first rule, a regex is performed on the body of the HTTP Response (possible if this Condition-Group is called from a Manipulation-Group) |
| ■ | In the second rule, a test is made on the first group found in the last regex (if found) |